Using pgAdmin4 as PostgreSQL editor
Hai semuanya, di materi kali ini kita akan membahas tentang pgAdmin4 sebagai editor untuk berinteraksi dengan PostgreSQL Database. Diantaranya adalah
- Connecting to a Server
- Developer Tools
- Managing Database Objects (Schema, Tables, User, etc)
- Backup and Restore
Ok langsung saja kita bahas materi yang pertama
Connecting to a Server
Before you can use the pgAdmin client to manage the objects that reside on your Postgres server, you must define a connection to the server.
You can (optionally) use the Server Group dialog to create server groups to organize the server connections within the tree control for easier management. To open the Server Group dialog, right-click on the Servers node of the tree control, and select Server Group from the Create menu.
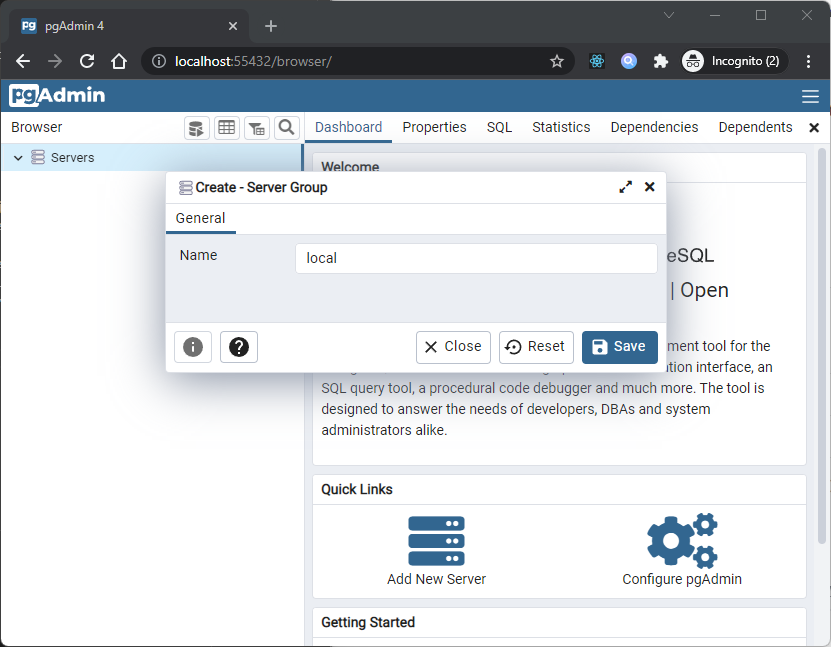
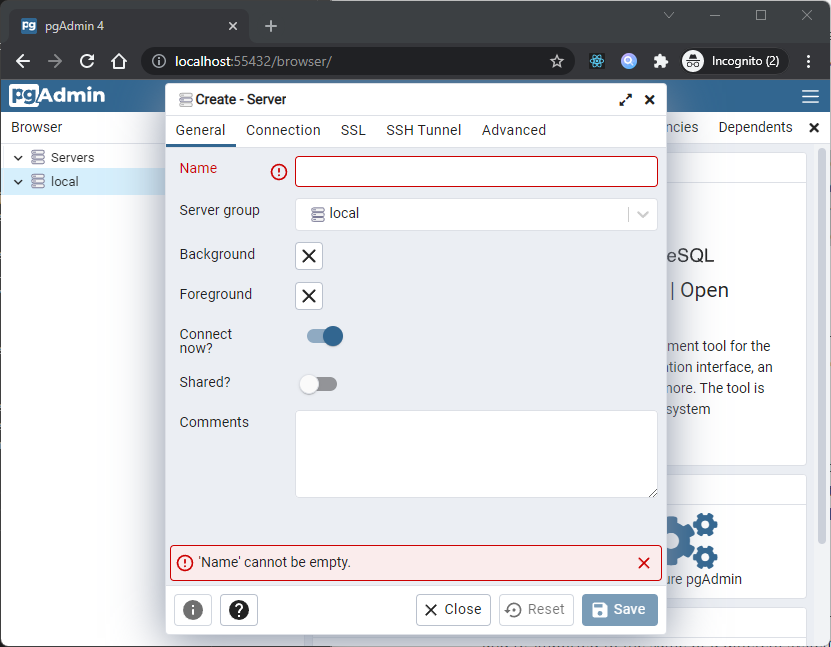
Use the fields on the Server dialog to define the connection properties for each new server that you wish to manage with pgAdmin. To open the Server dialog, right-click on the Servers node of the tree control, and select Server from the Create menu.
A master password is required to secure and later unlock saved server passwords. It is set by the user and can be disabled using config.
Server definitions (and their groups) can be exported to a JSON file and re-imported to the same or a different system to enable easy pre-configuration of pgAdmin.
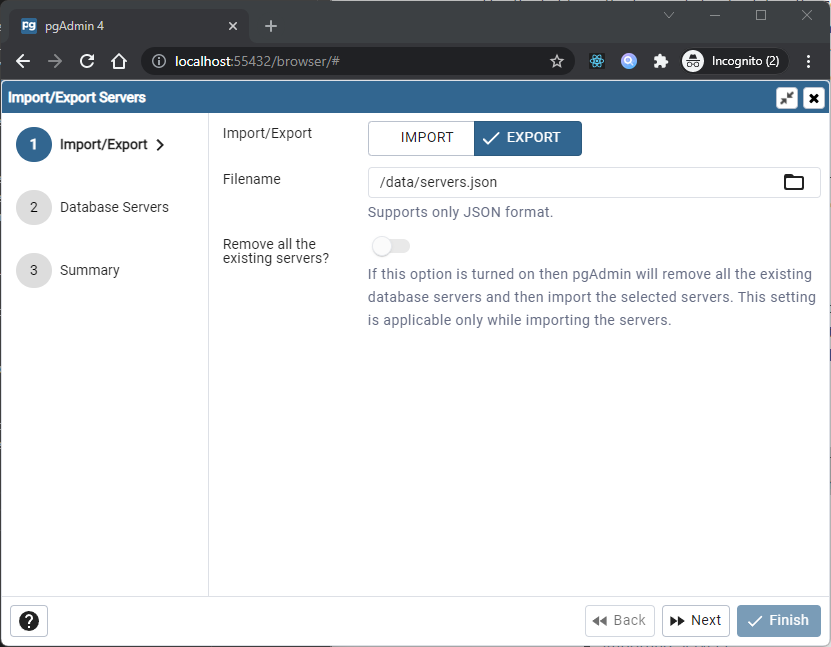
Developer Tools
The pgAdmin Tools menu displays a list of powerful developer tools that you can use to execute and analyze complex SQL commands, manage data, and debug PL/SQL code.
-
The Query Tool is a powerful, feature-rich environment that allows you to execute arbitrary SQL commands and review the result set. You can access the Query Tool via the Query Tool menu option on the Tools menu, or through the context menu of select nodes of the Browser tree control. The Query Tool allows you to:
- Issue ad-hoc SQL queries.
- Execute arbitrary SQL commands.
- Edit the result set of a SELECT query if it is updatable.
- Displays current connection and transaction status as configured by the user.
- Save the data displayed in the output panel to a CSV file.
- Review the execution plan of a SQL statement in either a text, a graphical format.
- View analytical information about a SQL statement.
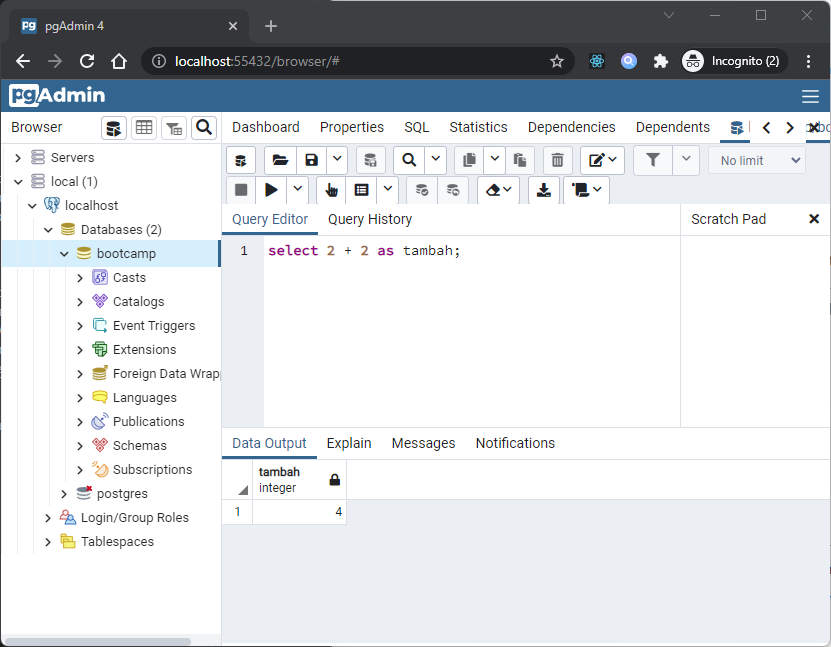
-
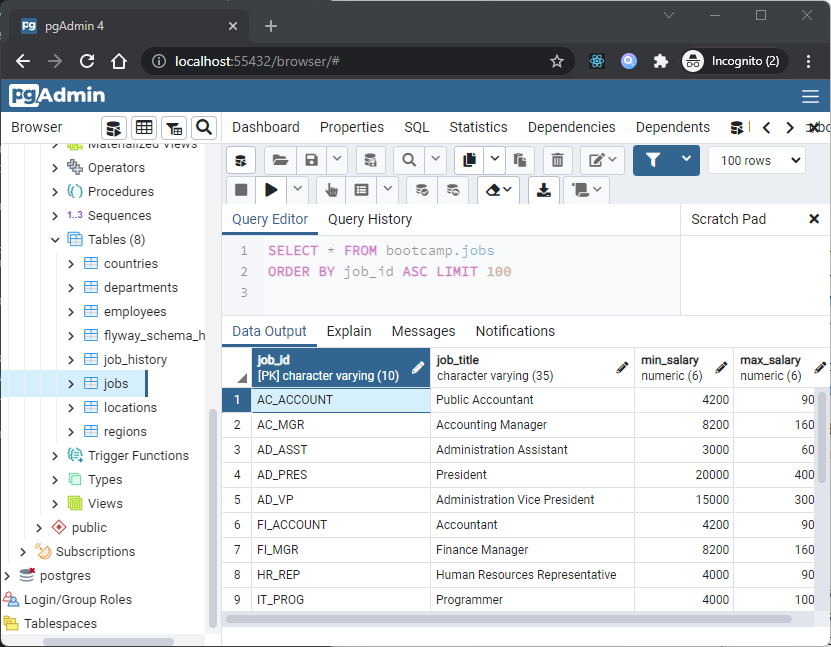
To view or modify data, right click on a table or view name in the Browser tree control. When the context menu opens, use the View/Edit Data menu to specify the number of rows you would like to display in the editor panel.
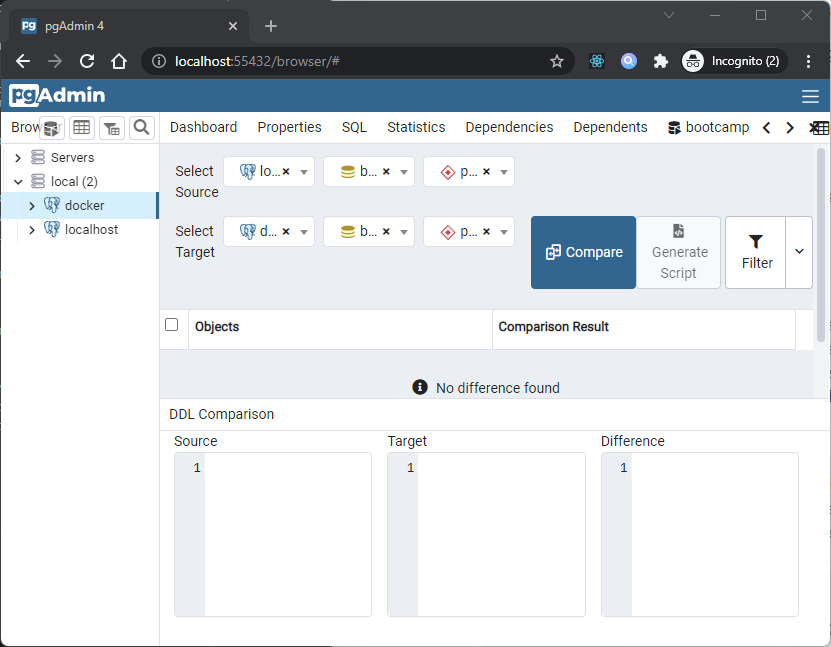
- Schema Diff is a feature that allows you to compare objects between two databases or two schemas. Use the Tools menu to access Schema Diff. The Schema Diff feature allows you to:
- Compare and synchronize the database objects (from source to target).
- Visualize the differences between database objects.
- List the differences in SQL statement for target database objects.
- Generate synchronization scripts.
-
The Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD) tool is a database design tool that provides a graphical representation of database tables, columns, and inter-relationships. ERD can give sufficient information for the database administrator to follow when developing and maintaining the database. The ERD Tool allows you to:
- Design and visualize the database tables and their relationships.
- Add notes to the diagram.
- Auto-align the tables and links for cleaner visualization.
- Save the diagram and open it later to continue working on it.
- Generate ready to run SQL from the database design.
- Generate the database diagram for an existing database.
- Drag and drop tables from browser tree to the diagram.
- The PSQL tool allows users to connect to PostgreSQL or EDB Advanced server using the psql command line interface through their browser. The PSQL tool is always available when pgAdmin is running in Desktop mode, but is disabled by default in Server mode.
- Open the PSQL tool from the Tools or browser tree context menu, or use PSQL tool button at the top of the browser tree.
- PSQL will connect to the current connected database from the browser tree.
Managing Database Objects
pgAdmin 4 provides simple but powerful dialogs that you can use to design and create database objects. Each dialog contains a series of tabs that you use to describe the object that will be created by the dialog; the SQL tab displays the SQL command that the server will execute when creating the object.
- Cast Dialog
- Collation Dialog
- Event Trigger Dialog
- Extension Dialog
- Foreign Table Dialog
- Function Dialog
- Package Dialog
- Procedure Dialog
- Publication Dialog
- Schema Dialog
- Sequence Dialog
- Subscription Dialog
- Synonym Dialog
- Trigger Function Dialog
- Type Dialog
- User Mapping Dialog
- View Dialog
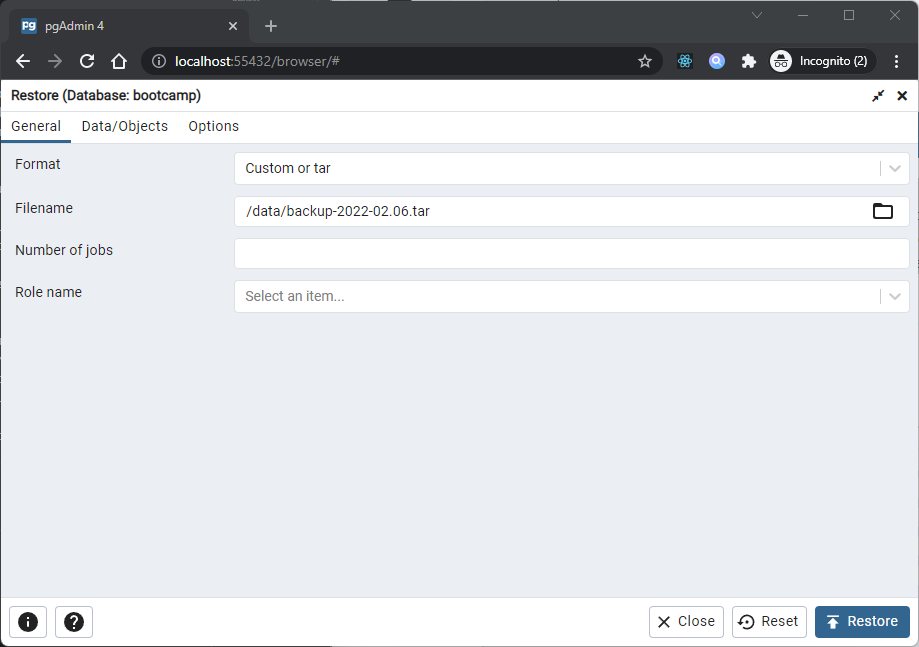
Backup and Restore
A powerful, but user-friendly Backup and Restore tool provides an easy way to use pg_dump, pg_dumpall, and pg_restore to take backups and create copies of databases or database objects for use in a development environment.
-
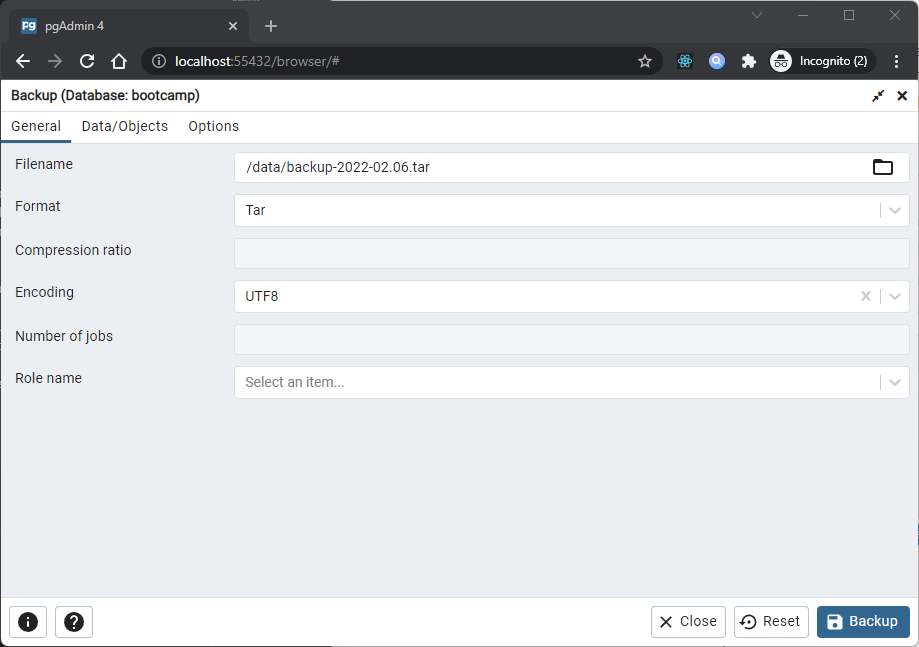
Backup Dialog, pgAdmin uses the pg_dump utility to provide an easy way to create a backup in a plain-text or archived format. You can then use a client application (like psql or the Query Tool) to restore a plain-text backup file, or use the Postgres pg_restore utility to restore an archived backup. The pg_dump utility must have read access to all database objects that you want to back up.
-
The Restore dialog provides an easy way to use a Custom, tar, or Directory format backup taken with the pgAdmin Backup dialog to recreate a database or database object. The Backup dialog invokes options of the pg_dump client utility; the Restore dialog invokes options of the pg_restore client utility.