- person Penulis:
-
 Dimas Maryanto
Dimas Maryanto
PT. Tabeldata Informatika
- account_balance_wallet Donasi via:
- Saweria a/n Dimas Maryanto
- lock_open Join Premium Members:
- Udemy.com
-
Daftar Materi
-
1. Pengenalan Docker 8
-
2. Docker Registry 3
-
3. Docker Container CLI 8
-
1. Docker CLI (Command Line Interface)
2. Management Docker Container
3. Management Docker Images
4. Run a command in a running container
5. Expose services to outside using ports
6. Copying files/content between container and filesystem
7. Logging, Inspect, & Resource Usage Statistics Containers
8. Run a Container using Environtment File
-
4. Docker Networks 7
-
5. Docker Volumes 5
-
6. Dockerfile 15
-
1. Build Docker Image Overview
2. Usage docker build
3. FROM Instruction
4. Environtment Replacement
5. Copying Resources
6. Excluding files/directories
7. Label Instruction
8. Execution Instruction
9. CMD vs ENTRYPOINT?
10. Exposing Ports
11. User, Volumes and Working Directory
12. Health Check Instruction
13. Multiple Stage Builds
14. Best practices for writing Dockerfiles
15. Best practices for scanning images
-
7. Study Kasus: Build docker image 14
-
1. Build specific docker image by programming languages
2. Build Docker Image for Java Webapp
3. Build Java Web using maven-docker-plugin
4. Build docker image for spring-boot
5. Springboot - using Environtment
6. Springboot - where data such as files/images we stored?
7. Springboot - Using Database
8. Build docker image for Angular Project
9. Angular - Access Rest API
10. Angular - Proxy to backend
11. Build docker image for PHP
12. Build Docker image for Laravel Framework
13. Laravel - Using Frontend & Rest API
14. Laravel - Using Database
-
8. Docker Compose 19
-
1. Overview of Docker Compose
2. Get started with Docker Compose
3. Overview of docker-compose CLI
4. Compose file specification and syntax
5. Environment variables in Compose
6. Volume in Compose
7. Share data between Containers in Compose
8. Using sshfs for share data in Compose
9. Using NFS for share data in Compose
10. Networking Overview in Compose file
11. Network links in Compose file
12. Specify custom networks in Compose file
13. Dependency between services in Compose file
14. Build docker image using Compose file
15. Using profiles with Compose file
16. Multiple Compose files to Add & Override attribute
17. Example use case of multiple compose files
18. Scale services using compose command
19. Use Compose in production
-
9. Study Kasus: Docker Compose 7
-
10. Docker Context 8
-
11. Study Kasus: Docker for CI 8
-
1. Overview of Study Cases using docker for CI
2. Setup environment for CI using Gitlab & Nexus OSS
3. The `.gitlab-ci.yml` file
4. Pipeline: PHP deployment using Gitlab CI
5. Pipeline: Java Web deployment using Gitlab CI
6. Pipeline: spring-boot deploy with Gitlab CI
7. Pipeline: Angular deploy with Gitlab CI
8. Pipeline: Laravel deploy with Gitlab CI
-
12. Docker Machine 7
-
13. Study Kasus: Ansible for Docker 4
-
14. Docker Swarm
- Materi: belum tersedia...
-
15. Study Kasus: Docker Swarm
- Materi: belum tersedia...
-
16. Docker on Cloud using GCP
- Materi: belum tersedia...
- Lastest Posts
-
 09 Apr 23
Working with Deployment object
09 Apr 23
Working with Deployment object
-
 26 Feb 23
Study cases: Microservice apps (...
26 Feb 23
Study cases: Microservice apps (...
-
 05 Feb 23
Welcome to the Nutanix HCF (Hybr...
05 Feb 23
Welcome to the Nutanix HCF (Hybr...
-
 04 Feb 23
Silabus SRE - Nutanix AHV: Pemul...
04 Feb 23
Silabus SRE - Nutanix AHV: Pemul...
-
 17 Jan 23
What is Workload Resources?
17 Jan 23
What is Workload Resources?
-
 17 Jan 23
Overview Kubernetes Workloads re...
17 Jan 23
Overview Kubernetes Workloads re...
-
 15 Jan 23
Getting started with Transaction...
15 Jan 23
Getting started with Transaction...
-
 14 Jan 23
Overview of Concurrency Control
14 Jan 23
Overview of Concurrency Control
-
 14 Jan 23
Time your practice (part 3)
14 Jan 23
Time your practice (part 3)
-
 08 Jan 23
Cleanup Data from Table
08 Jan 23
Cleanup Data from Table
Dashboard using Docker Desktop
Hai semuanya, di materi kali ini kita akan membahas tentang dashboard menggunakan Docker Dekstop, Diantaranya sebagai berikut:
- Docker desktop overview
- Explore running containers and applications
- Interact with containers and applications
- Explore docker images
- Explore volumes
Ok langsung aja kita ke pembahasan pertama yaitu
Docker desktop overview
Docker Desktop is an easy-to-install application for your Mac or Windows environment that enables you to build and share containerized applications and microservices. Docker Desktop includes Docker Engine, Docker CLI client, Docker Compose, Docker Content Trust, Kubernetes, and Credential Helper.
Notes Professional use of Docker Desktop in large organizations (more than 250 employees or more than $10 million in annual revenue) requires users to have a paid Docker subscription. While the effective date of these terms is August 31, 2021, there is a grace period until January 31, 2022 for those that require a paid subscription. For more information, see Docker Desktop License Agreement.
Some of the key features of Docker Desktop include:
- Ability to containerize and share any application on any cloud platform, in multiple languages and frameworks
- Easy installation and setup of a complete Docker development environment
- Includes the latest version of Kubernetes
- Automatic updates to keep you up to date and secure
- On Windows, the ability to toggle between Linux and Windows Server environments to build applications
- Fast and reliable performance with native Windows Hyper-V virtualization
- Ability to work natively on Linux through WSL 2 on Windows machines
- Volume mounting for code and data, including file change notifications and easy access to running containers on the localhost network
- In-container development and debugging with supported IDEs
Explore running containers and applications
From the Docker menu, select Dashboard. This lists all your running containers and applications. You must have running or stopped containers and applications to see them listed on the Docker Dashboard.
Same as using docker command line
docker container ls -aStarting container from docker command
Seperti yang kita telah pelajari, untuk menjalankan container kita bisa menggunakan terminal/commandpromt dengan menggunakan perintah seperti berikut
docker run -d -e POSTGRES_PASSW0RD=testPasswordRoot postgres:12.6the result look’s like this:
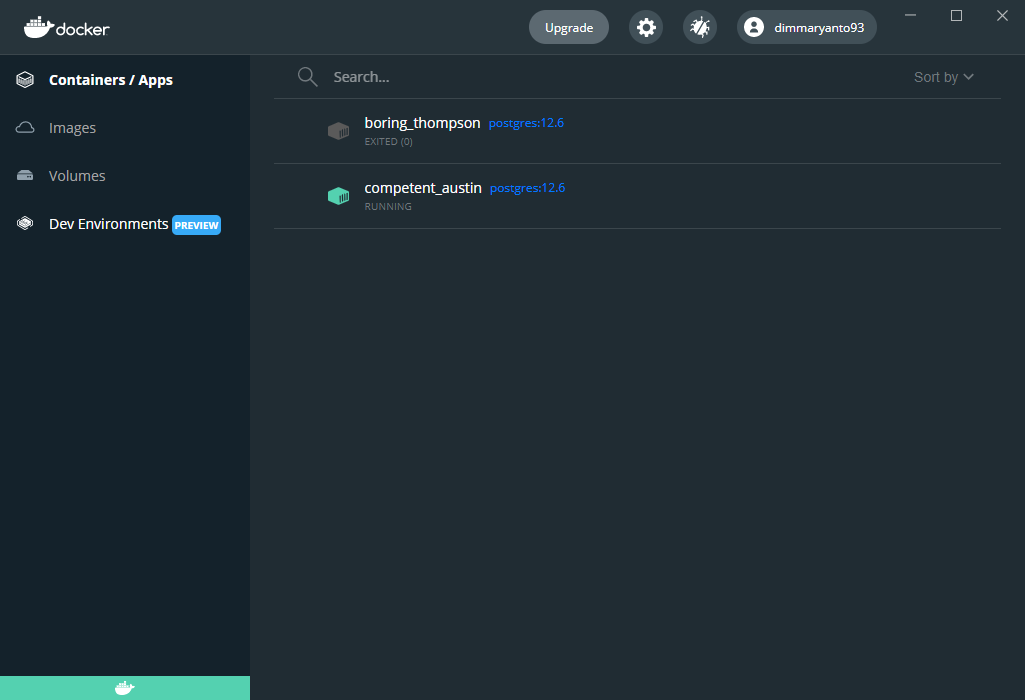
Starting container from docker-compose
Sama halnya dengan perintah docker-compose ps docker-desktop juga bisa menampilkan detail list containernya, Sekarang coba jalankan compose file seperti berikut
docker-compose --project-directory .\08-docker-compose\10-scale\ up -d --scale backend=3the result look’s like this:
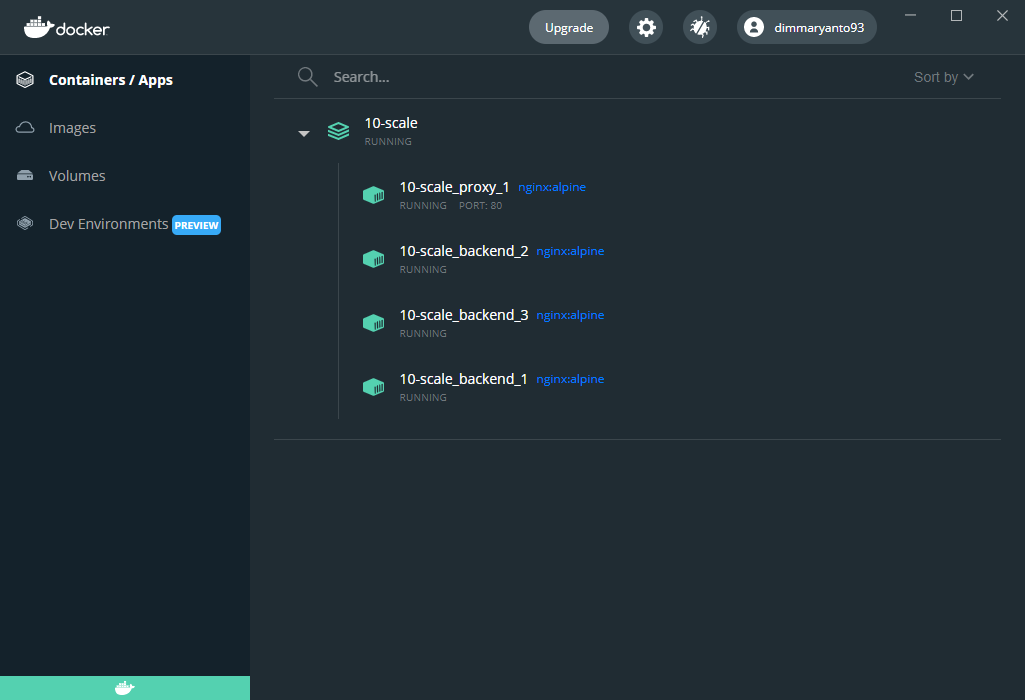
Now that you can see the list of running containers and applications on the Dashboard, let us explore some of the actions you can perform:
- Click
Portto open the port exposed by the container in a browser. - Click
CLIto open a terminal and run commands on the container. If you have installed iTerm2 on your Mac, the CLI option opens an iTerm2 terminal. Otherwise, it opens the Terminal app on Mac, or a Command Prompt on Windows. - Click
Stop,Start,Restart, orDeleteto perform lifecycle operations on the container. - Use the Search option to search for a specific object. You can also sort your containers and applications using various options. Click the
Sort bydrop-down to see a list of available options.
Interact with containers and applications
From the Docker Dashboard, select the example application we started earlier.
The Containers/Apps view lists all the containers running on the application and contains a detailed logs view. It also allows you to start, stop, or delete the application. Use the Search option at the bottom of the logs view to search application logs for specific events, or select the Copy icon to copy the logs to your clipboard.
Click on a specific container for detailed information about the container. The container view displays Logs, Inspect, and Stats tabs and provides quick action buttons to perform various actions.
- Select Logs to see logs from the container. You can also search the logs for specific events and copy the logs to your clipboard.
- Select Inspect to view low-level information about the container. You can see the local path, version number of the image, SHA-256, port mapping, and other details.
- Select Stats to view information about the container resource utilization. You can see the amount of CPU, disk I/O, memory, and network I/O used by the container.
Explore docker images
The Images view is a simple interface that lets you manage Docker images without having to use the CLI. By default, it displays a list of all Docker images on your local disk. To view images in remote repositories, click Sign in and connect to Docker Hub. This allows you to collaborate with your team and manage your images directly through Docker Desktop.
The Images view allows you to perform core operations such as running an image as a container, pulling the latest version of an image from Docker Hub, pushing the image to Docker Hub, and inspecting images.
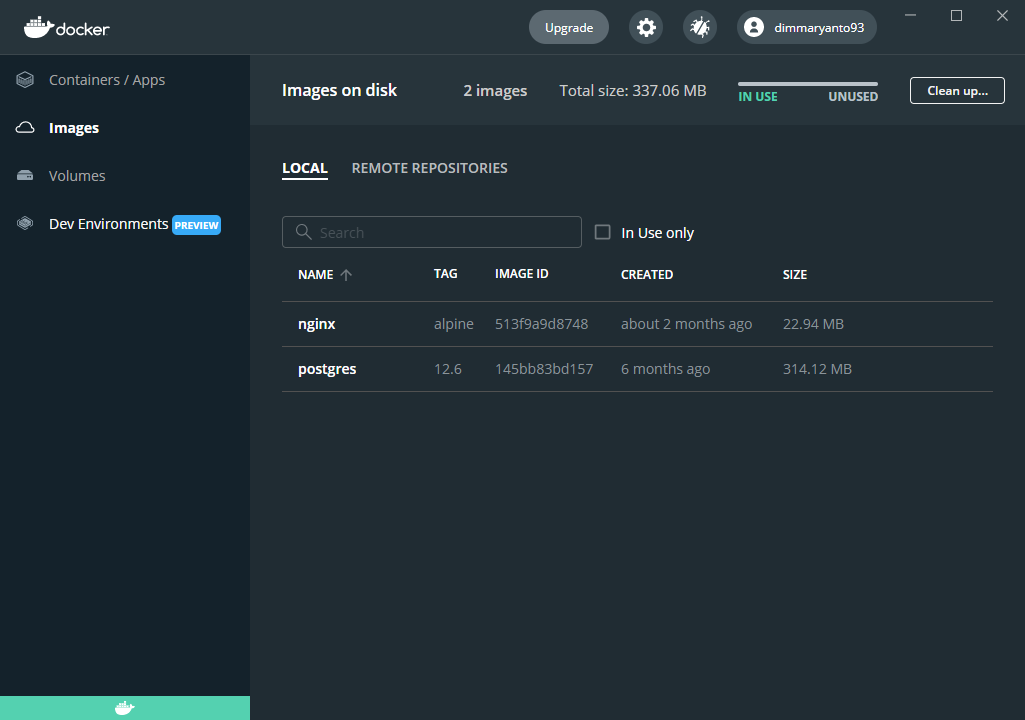
Interact with remote repositories
The Images view also allows you to manage and interact with images in remote repositories and lets you switch between organizations. Select an organization from the drop-down to view a list of repositories in your organization.
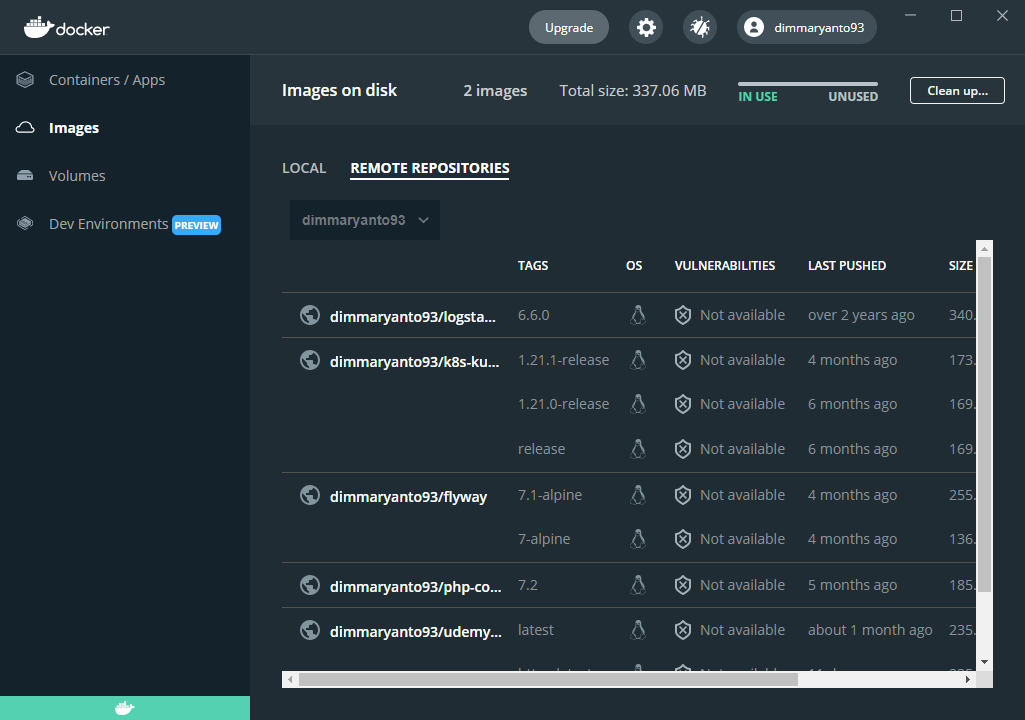
Explore volumes
You can use volumes to store files and share them among containers. Volumes are created and are directly managed by Docker. They are also the preferred mechanism to persist data in Docker containers and services.
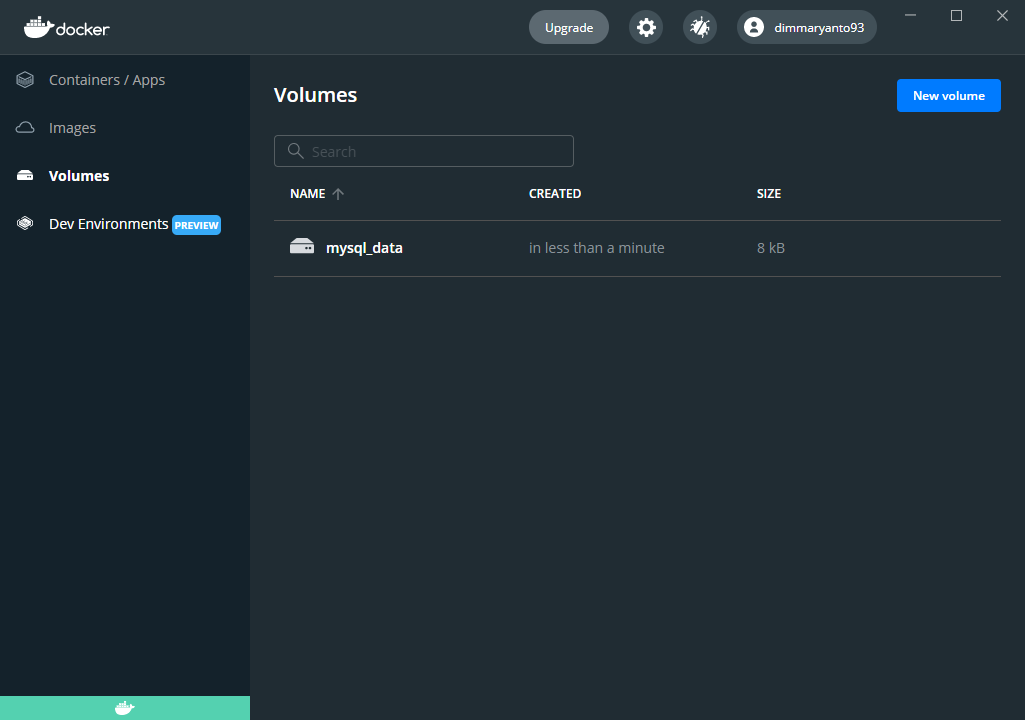
Yuk simak juga videonya,
Dan jika temen-temen belajar hal baru kali ini jangan lupa buat Like, Subcribe, dan Share ke temen kalian. Terimakasih!!!

